HealthCare, Cancer, WingsMed
Cancer Made Simple: The 4 Major Types You Should Know.!
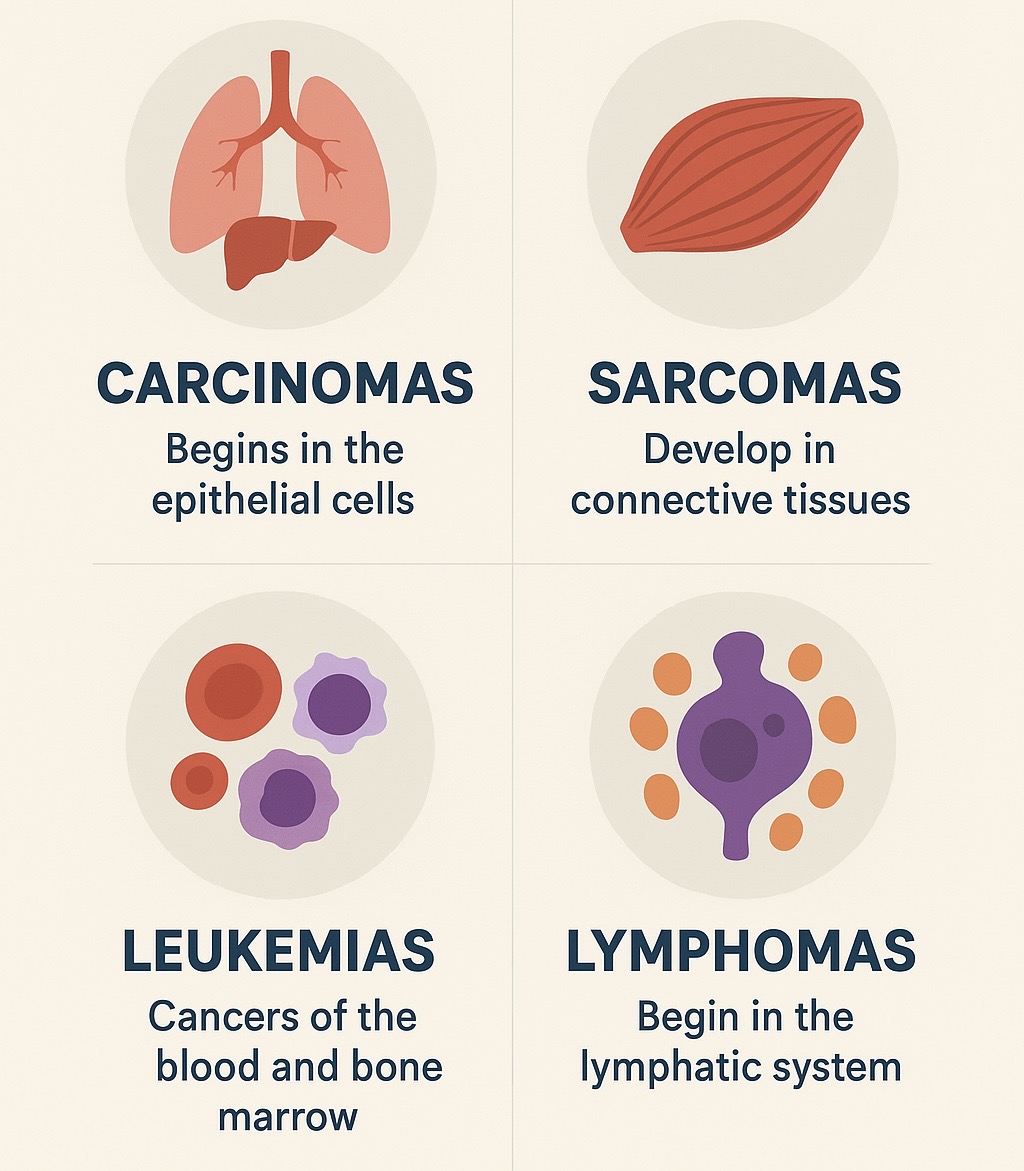
Cancer is one of the leading health challenges across the world. While there are more than 100 different kinds of cancer, doctors and researchers classify them into four major types based on the kind of cells from which they develop.
Understanding these categories helps in better diagnosis, treatment planning, and awareness.
1. Carcinomas
Carcinomas are the most common type of cancer. They begin in the epithelial cells, which line the skin and the tissues of internal organs. Because epithelial cells cover most parts of the body, carcinomas can appear in many places, such as the lungs, breast, prostate, pancreas, and colon.
✔️ Examples: Breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer.
✔️ Characteristics: Usually form solid tumors and may spread through the lymph nodes or bloodstream.
2. Sarcomas
Sarcomas are relatively rare compared to carcinomas. They develop in the body’s connective tissues such as bones, muscles, fat, cartilage, and blood vessels.
✔️ Examples: Osteosarcoma (bone cancer), liposarcoma (fat tissue), leiomyosarcoma (smooth muscle).
✔️ Characteristics: Often appear as lumps or swellings in bones or soft tissues and may grow quickly.
3. Leukemias
Leukemias are cancers of the blood and bone marrow. Unlike carcinomas and sarcomas, leukemias do not form solid tumors. Instead, they cause the production of abnormal white blood cells, which crowd out normal blood cells and weaken the body’s immune system.
✔️ Examples: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
✔️ Characteristics: Symptoms often include fatigue, frequent infections, bruising, and bleeding.
4. Lymphomas
Lymphomas begin in the lymphatic system, a vital part of the immune system that helps fight infections. They affect lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell).
✔️ Examples: Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
✔️ Characteristics: Swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss are common symptoms.
Conclusion
Although there are many different cancers, carcinomas, sarcomas, leukemias, and lymphomas represent the four major categories.
Knowing these distinctions is crucial for early detection and proper treatment. With continuous medical research and improved therapies, survival rates are steadily improving, making awareness and timely diagnosis more important than ever.